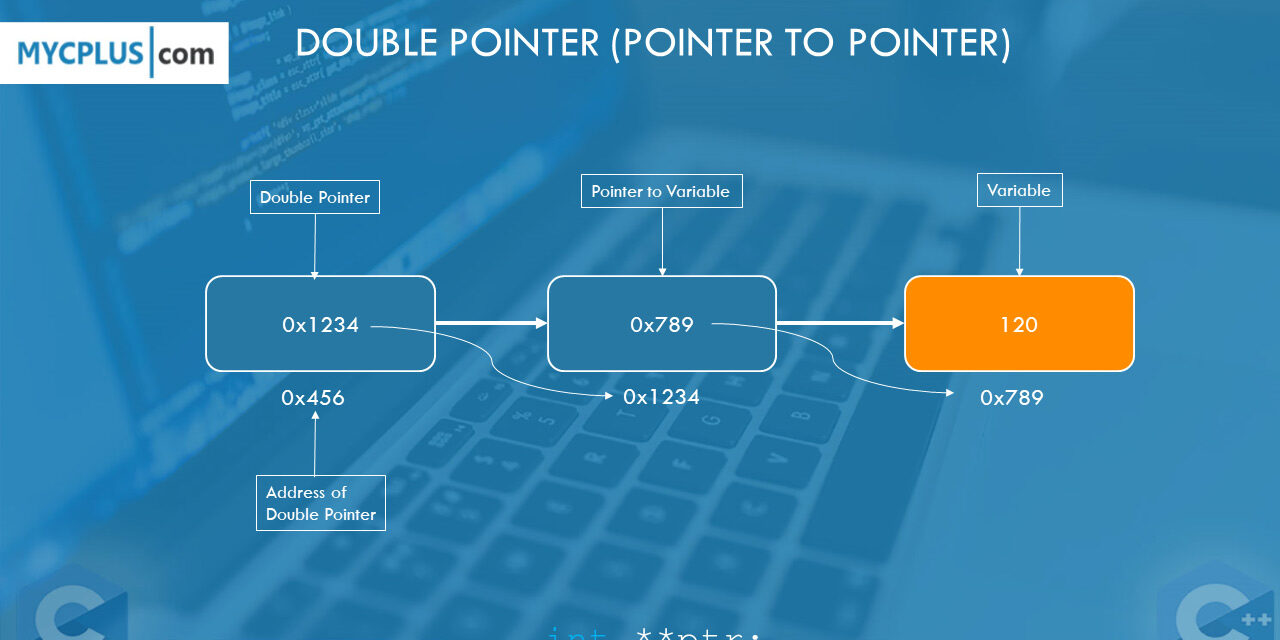
In C programming, a double pointer is a pointer that points to another pointer. It is also referred to as a pointer-to-pointer. A pointer in C is a variable that represents the location of an item, such as a variable or an array. We use pointers to pass information back and forth between a function and its reference point.
Sometimes, a pointer can be declared to point to another pointer which points to a variable. Here, the first pointer contains the address of the second pointer. The second pointer points to an actual memory location where the data is stored, i.e. a variable. That’s the reason why we also call such pointers as double pointers.
Table of Contents
- How to declare a pointer-to-pointer?
- How to initialize a double pointer?
- C Program to show how double pointer works?
- Use Double Pointer to create Two Dimensional Array
- Uses of Pointer-to-Pointer (Double Pointer)
- Common Errors with Double Pointers in C
How to declare a pointer-to-pointer?
The syntax to declare a double pointer in C is:
1 | int **doubleptr; |
In this example, the variable doubleptr is a double pointer to an integer value. The ** notation is used to indicate that doubleptr is a pointer to a pointer. To initialize a double pointer, you can use the address of operator & on a pointer variable, like this:
How to initialize a double pointer?
1 2 3 4 5 6 | int *ptr; int **pptr; ptr = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)); *ptr = 10; pptr = &ptr; |
C Program to show how double pointer works?
The following C program shows how pointer-to-pointer works by printing the pointer address as well as variable address and values:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | #include <stdio.h> int main() { int var = 120; int *varptr = &var; int **doubleptr = &varptr; printf("Value of var = %d\n", var ); printf("Value of var pointer = %d\n", *varptr ); printf("Value of double pointer = %d\n", **doubleptr); printf("Address of var = %p\n", &var ); printf("Address of var pointer = %p\n", &varptr ); printf("Value in var pointer = %p\n", varptr ); printf("Address of double pointer = %p\n", *doubleptr); printf("Value in double pointer = %p\n", doubleptr); return 0; } |
The output of the above C Program is:
Value of var = 120
Value of var pointer = 120
Value of double pointer = 120
Address of var = 0x7ffe25192bfc
Address of var pointer = 0x7ffe25192c00
Value in var pointer = 0x7ffe25192bfc
Address of double pointer = 0x7ffe25192bfc
Value in double pointer = 0x7ffe25192c00
Use Double Pointer to create Two Dimensional Array
Here is an example that demonstrates how to use double pointers to create a dynamic two-dimensional array. This program demonstrates how double pointers can be used to create complex data structures with dynamic memory allocation in C programming.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { int rows, cols, i, j; int **matrix; printf("Enter the number of rows: "); scanf("%d", &rows); printf("Enter the number of columns: "); scanf("%d", &cols); // Allocate memory for the matrix matrix = (int **)malloc(rows * sizeof(int *)); for (i = 0; i < rows; i++) { matrix[i] = (int *)malloc(cols * sizeof(int)); } // Fill the matrix with values for (i = 0; i < rows; i++) { for (j = 0; j < cols; j++) { matrix[i][j] = i * j; } } // Print the matrix for (i = 0; i < rows; i++) { for (j = 0; j < cols; j++) { printf("%d ", matrix[i][j]); } printf("\n"); } // Free the memory for (i = 0; i < rows; i++) { free(matrix[i]); } free(matrix); return 0; } |
This program prompts the user to enter the number of rows and columns for a matrix (two dimensional array), then dynamically allocates memory for the matrix using double pointers. It fills the matrix with values, prints it to the console, and then frees the memory.
Uses of Pointer-to-Pointer (Double Pointer)
Double pointers serve a variety of purposes in C Programming. Here are some of the most common uses of double pointers and why you might want to use them:
- Dynamic Memory Allocation: Double pointers are often used to allocate memory for arrays, particularly multi-dimensional arrays. By using a double pointer, you can ensure that the memory allocation is protected even outside of a function call. To allocate space for a matrix or multi-dimensional arrays dynamically, you will need a double-pointer.
- Passing Handles Between Functions: This is particularly useful if you need to pass re-locatable memory between functions.
- Characters List: Another use is that if you want to have a list of characters (a word), you can use char *word, for a list of words (a sentence), you can use char **sentence, and for list of sentences (a paragraph), you can use char ***paragraph.
- Main Function Parameters: One of the most common uses (every C programmer should have encountered) as parameters to the main() function, i.e. int main(int argc, char **argv). Here argv is the array of arguments passed on to this program.
- Linked Lists: Double pointers are frequently used in linked list operations, such as insertion and deletion.
If you’re interested in learning more about double pointers, there are many helpful resources available online. You might start by reading some of the articles on StackOverflow or Quora.
Common Errors with Double Pointers in C
Here are some common errors with double pointers that new programmers make while write C Programming code:
- Incorrect Syntax: One common mistake when working with double pointers is using the wrong syntax. This can result in compilation errors or unexpected behavior in the program. For example, forgetting to include the ‘*’ operator when dereferencing a double pointer can cause the program to crash.
- Dereferencing Errors: Another common error is dereferencing incorrectly. This can happen when trying to access memory that hasn’t been allocated or has already been freed. Forgetting to check for NULL values can also lead to segmentation faults.
- Memory Allocation Errors: Double pointers are often used for dynamic memory allocation in C programming, but errors can occur when allocating memory. Common mistakes include not allocating enough memory, allocating too much memory, or failing to free memory when it’s no longer needed.
- Type Mismatch Errors: Double pointers can also cause type mismatch errors if they’re not properly cast to the correct type. This can happen when passing double pointers to functions or when assigning values to double pointers.
- Pointer Arithmetic Errors: Pointer arithmetic can be tricky in C programming, especially when working with double pointers. Common errors include using incorrect operators or not correctly accounting for the size of the data type.
By avoiding these common errors with double pointers in C programming, you can write better C programs. This will also help to improve your overall understanding of double pointers and enhance your programming skills further.
Here’s Must-Read List of C programming books for beginners
C Programming Language, 2nd Edition
With over 600 5-star reviews on Amazon, readers agree that C Programming Language, 2nd Edition by Brian Kernighan and Dennis Ritchie is the best C Programming book for Beginners. The authors present the complete guide to ANSI standard C language programming. Written by the developers of C, this new version helps readers keep up with the finalized ANSI standard for C while showing how to take advantage of C’s rich set of operators, economy of expression, improved control flow, and data structures.
21st Century C: C Tips from the New School
Throw out your old ideas about C and get to know a programming language that’s substantially outgrown its origins. With this revised edition of 21st Century C, you’ll discover up-to-date techniques missing from other C tutorials, whether you’re new to the language or just getting reacquainted.
C Programming Absolute Beginner’s Guide
Greg Perry is the author of over 75 computer books and known for bringing programming topics down to the beginner’s level. His book C Programming Absolute Beginner’s Guide, is today’s best beginner’s guide to writing C programs–and to learning skills to use with practically any language. Its simple, practical instructions will help you start creating useful, reliable C code, from games to mobile apps. Plus, it’s fully updated for the new C11 standard and today’s free, open source tools!
C Programming: A Modern Approach, 2nd Edition
KN King tackles on some C standard library specifics header by header in his C Programming: A Modern Approach book. The second edition maintains all the book’s popular features and brings it up to date with coverage of the C99 standard. The new edition also adds a significant number of exercises and longer programming projects, and includes extensive revisions and updates.
Programming Arduino: Getting Started with Sketches
Simon Monk, a Ph.D. in software engineering, writes this great little book for learning to program the arduino using C language. This bestselling guide explains how to write well-crafted sketches using Arduino’s modified C language. You will learn how to configure hardware and software, develop your own sketches, work with built-in and custom Arduino libraries, and explore the Internet of Things—all with no prior programming experience required!